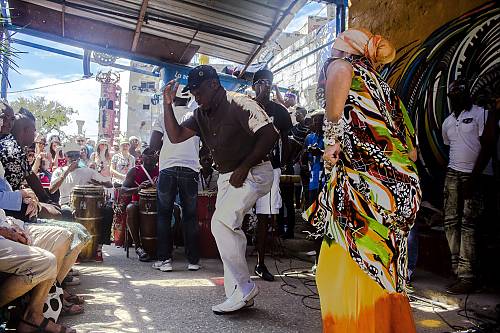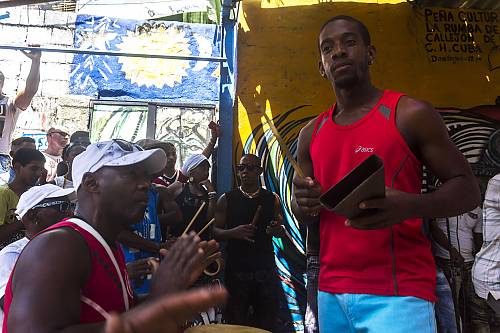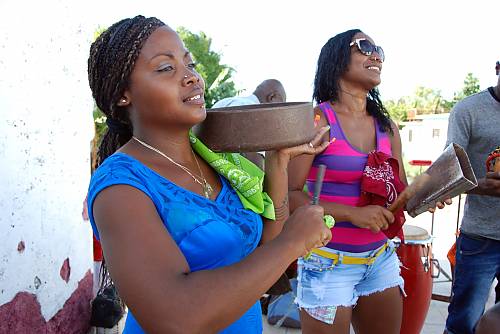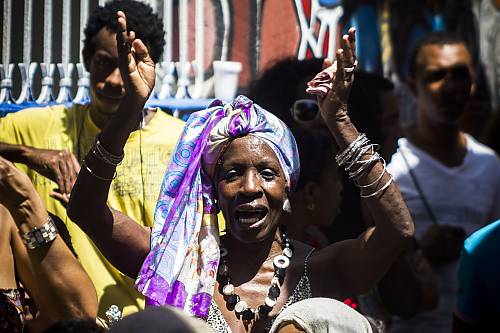Rumba in Cuba, a festive combination of music and dances and all the practices associated
Inscribed in 2016 (11.COM) on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity

The music and movements of rumba in Cuba are mainly associated with African culture but also feature elements from Antillean culture and Spanish flamenco. Historically, rumba in Cuba developed in marginal neighbourhoods of cities in Cuba like Havana and Matanzas, near other ports and shanty towns and grew especially popular in rural areas where communities of African slaves lived. Spreading from the west to the east of the country, it has been a major symbol of a marginal layer of Cuban society and identity, acting as an expression of self-esteem and resistance and tool for social outreach, helping to enrich the lives of practising communities. Performances consist of verbal and non-verbal forms of communication such as chants, gestures, handclapping, dance and specific body language. Instruments, either percussion or simply utensils from the home or work, are part of the practice. A festive atmosphere develops where the performers, working within specific cultural codes, and the audience begin to interact. The dances and chants evoke a sense of grace, sensuality and joy that aims to connect people, regardless of their social and economic background, gender or ethnicity. The practice of rumba in Cuba has been transmitted over generations by imitation within families and neighbourhoods.